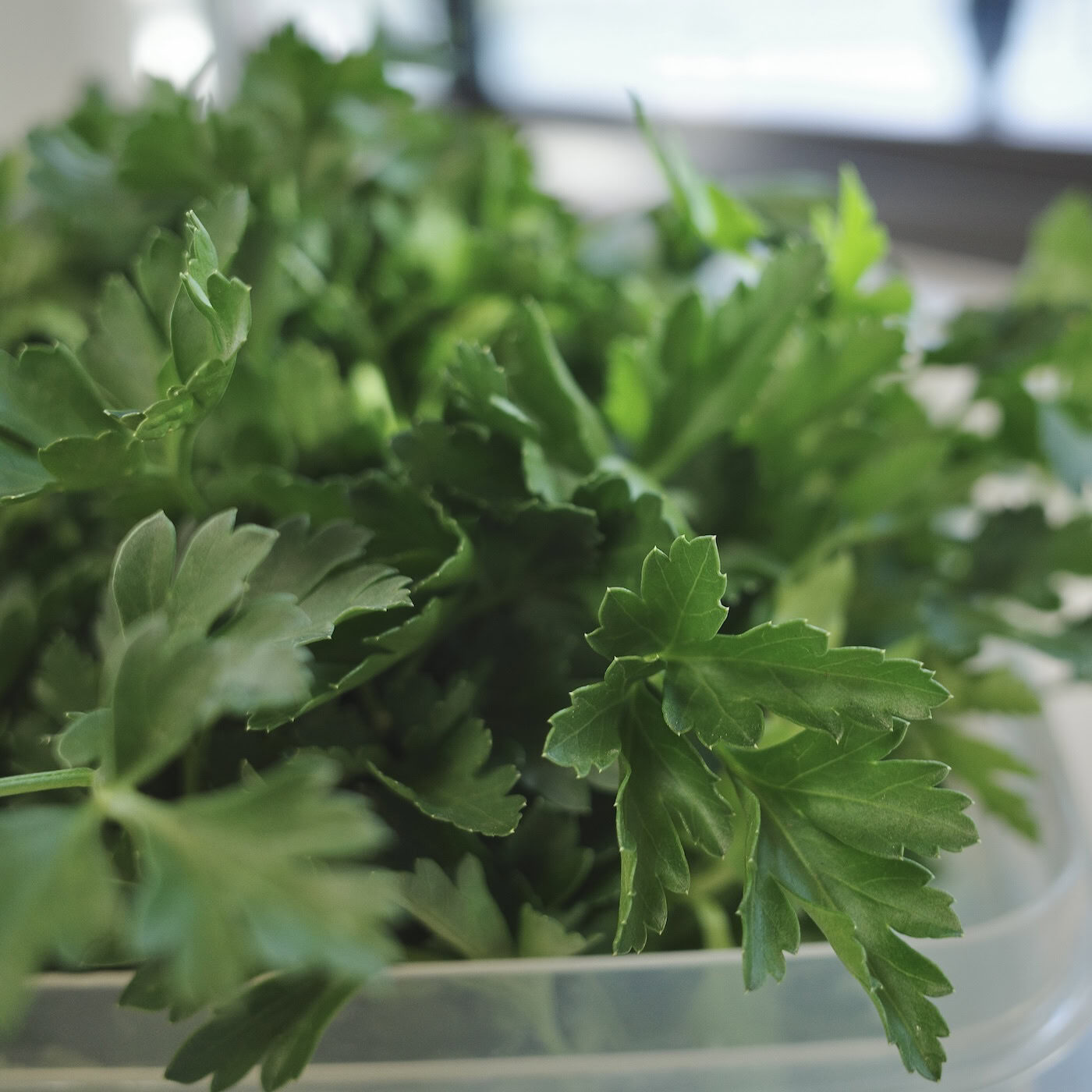
Parsley
Parsley is the herb derived from the leaves and shoots of Petroselinum crispum, a biennial in the parsley family. There are two primary culinary varieties:
Flat-leaf Parsley: Petroselinum crispum var. neapolitanum (pictured)
Curly-leaf Parsley: Petroselinum crispum var. crispum
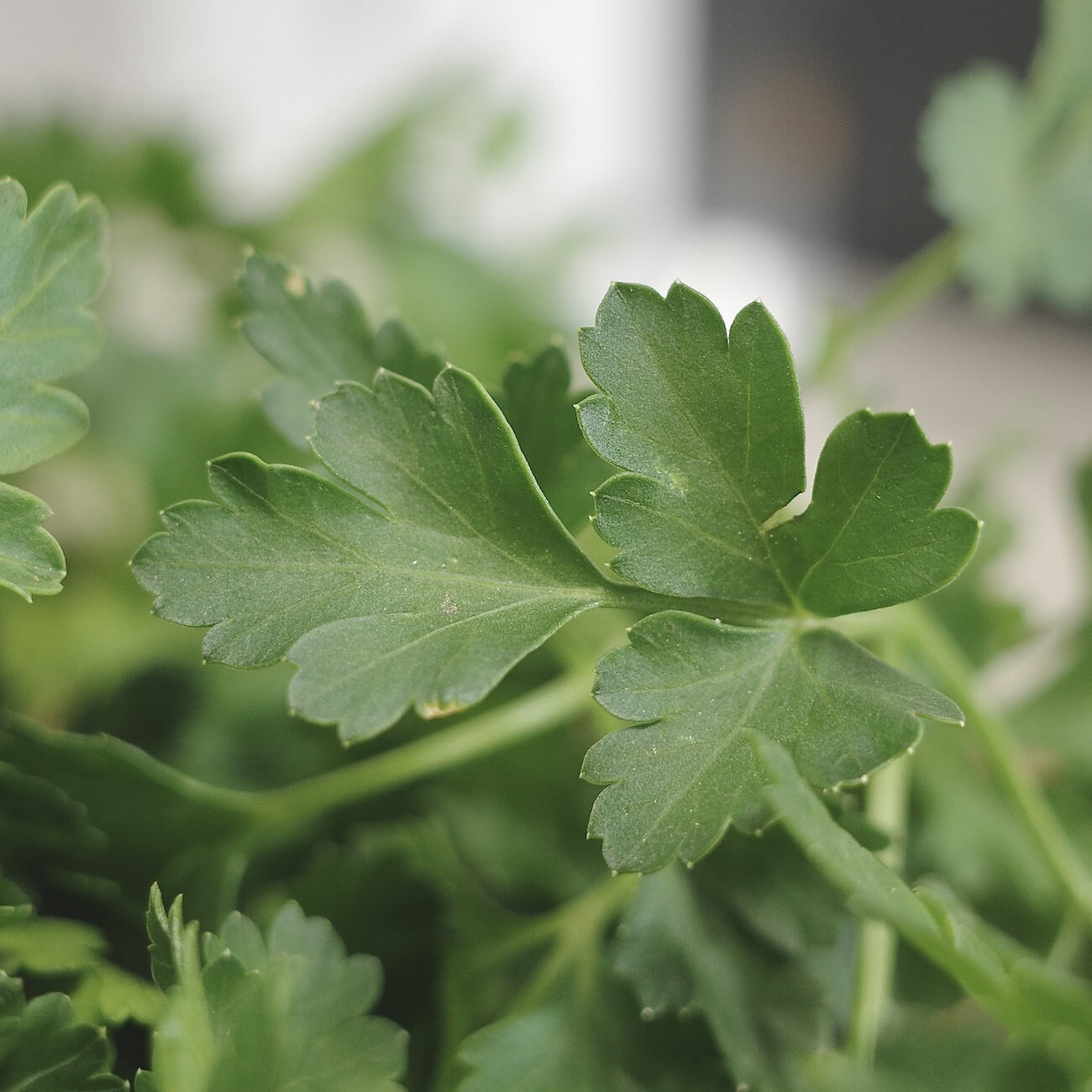

REGION OF ORIGIN
The Mediterranean. Italy, Greece, Algeria, and Tunisia played especially important roles in parsley's original cultivation and use. It’s a highly adaptable herb and now grows in many climates around the globe.
PART & COLOR
Parsley is primarily used for its vibrant leaves, which range from almost neon green to a deeper, darker green based on the variety. Curly-leaf parsley leaves are tightly curled, looking frillier than the broader, smoother, glossier flat-leaf parsley. When dried, parsley loses its brightness, becoming a duller green. It also produces small, yellow-green edible flowers.
HARVEST
Parsley is a biennial herb, but it is often grown as an annual to be harvested in its first year. It can be sown in early spring or late summer, preferring full sun to partial shade. Harvesting can begin as soon as the plant has enough leaves to spare. To ensure a steady supply of leaves, harvest the outer stems first, cutting them close to the base. Try not to cut more than a third of the plant at a time to encourage healthy regrowth.
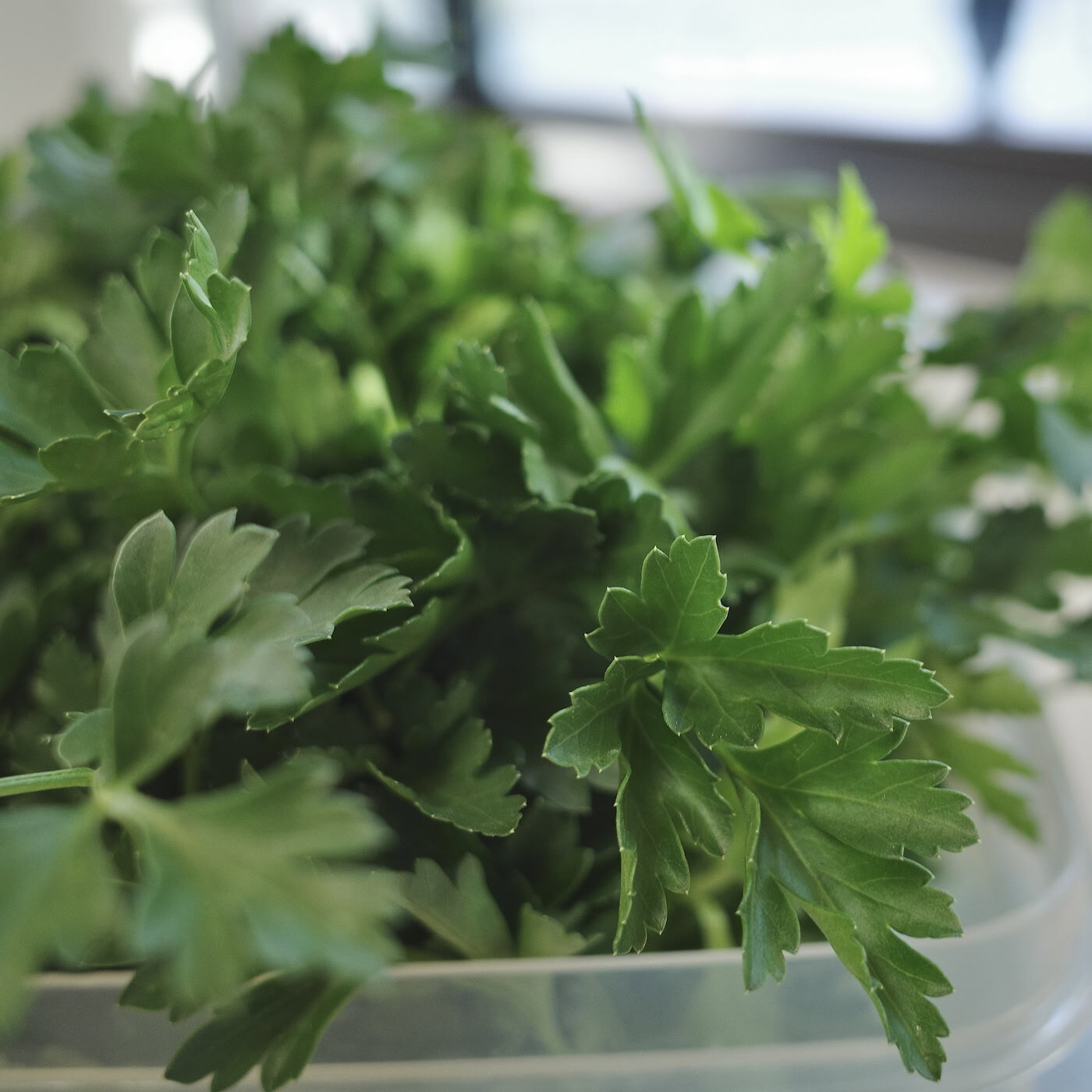

FLAVOR & AROMA PROFILE
Parsley's aroma is clean and green. It has a freshness reminiscent of spring meadows—grassy with subtle notes of citrus, anise, mint, and pepper. The scent is invigorating and light, which is why it sees such widespread use. When freshly chopped, the leaves release a burst of energizing aromatics.
The flavor of parsley carries these notes as well. Its refreshing, subtle tang blends so well with other ingredients without overpowering them. Yet it’s distinct enough to be noted and appreciated. Flat-leaf parsley is known for its stronger flavor, while the curly-leaf variety is milder and mainly used as a garnish due to its beautiful ruffled leaves.
CULINARY USES
Finely chopped parsley is often sprinkled on soups, salads, pastas, roasted meats, and vegetables. It's a primary ingredient in sauces like Argentinian chimichurri and Italian gremolata, and is sometimes added to modern takes on pesto. Fresh parsley is often mixed into stuffings for poultry to contrast its brightness against the savory elements. It’s also popular to incorporate it into butters and oils.
Fresh parsley is preferred for its vibrant top notes, but its dried form is used in seasoning blends and rubs. It's typically used in recipes with long cooking times so that it's concentrated flavor can slowly release into the other ingredients.